Load Balancer is a virtual machine or appliance that balances your web application load that could be Http or Https traffic that you are getting in. It balances a load of multiple web servers so that no web server gets overwhelmed.
By Amazon:-
Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, IP addresses, and Lambda functions. It can handle the varying load of your application traffic in a single Availability Zone or across multiple Availability Zones. Elastic Load Balancing offers three types of load balancers that all feature the high availability, automatic scaling, and robust security necessary to make your applications fault tolerant.
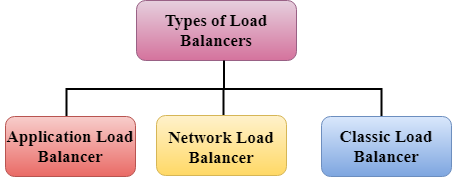
Application Load Balancer
- An Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched a new load balancer known as an Application load balancer (ALB) on August 11, 2016.
- It is used to direct user traffic to the public AWS cloud.
- It identifies the incoming traffic and forwards it to the right resources. For example, if a URL has /API extensions, then it is routed to the appropriate application resources.
- It is operated at Layer 7 of the OSI Model.
- It is best suited for load balancing of HTTP and HTTPs traffic.
- Application load balancers are intelligent, sending specific requests to specific web servers.
- If we take an example of TESLA. We have three models of TESLA, i.e., TESLA Model X, TESLA Model S, and TESLA Model 3 and TESLAs have onboard computing facility. You will have a group of web servers that serve the Model X, a group of web servers that serve the Model S, and similarly for Model 3. We have one Load balance that checks whether the incoming traffic comes from either Model X, Model S or Model 3, and then sends it to the intended froup of servers.
Network Load Balancer
- It is operated at the Layer 4 of the OSI model.
- It makes routing decisions at the transport layer (TCP/SSL), and it can handle millions of requests per second.
- When a load balancer receives a connection, it then selects a target from the target group by using a flow hash routing algorithm. It opens the TCP connection to the selected target of the port and forwards the request without modifying the headers.
- It is best suited for load balancing the TCP traffic when high performance is required.
Classic Load Balancer
- It is operated at Layer 4 of the OSI model.
- It routes the traffic between clients and backend servers based on IP address.
- For example, an Elastic Load balancer receives a request from a client on TCP port 80, it will then routes the request to a specified port of backend servers. The port on which the Load Balancer routes to the target server will be having port number 80. The backend server will then send the requested data back to the ELB, which will then forward the Backend server reply to the client. According to the client's perspective, the request has been fulfilled by the ELB, not by the backend server.
- Classic Load balancers are legacy Elastic load balancers.
- It can also be used for load balancing the HTTP or HTTPs traffic and use layer 7-specific features, such as X-forwarded and sticky sessions.
- You can also use the Layer 4 load balancing for applications that rely purely on the TCP protocol.
Load Balancer Errors
- Classic Load Balancer
If you get an error 504, this is a gateway timeout error. A Load balancer is still available, but it has a problem in communicating with the EC2 instance. If your application stops responding, the ELB (Classic Load Balancer) responds with a 504 error. This means that the application is having issues and it could be either at the web server layer or the Database layer.
In order to troubleshoot where the application is failing, and scale it up or out where possible.
X-Forwarded-For-Header
The X-Forwarded-For-Header is used to determine the IP address of a client when you use a classic load balancer.
Working of X-Forwarded-For-Header
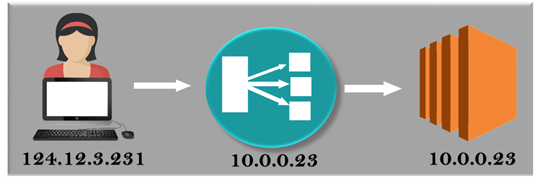
- A user is on the Ipv4 address, i.e., 124.12.3.23.
- A user is sending a request to the classic load balancer which in turn folded the request into an EC2 instance. An EC2 instance is going to use the private address, i.e., 10.0.0.23 and this is the only address which is seen by an EC2 instance.
- An EC2 instance is capturing only private address as Classis Load balancer encompasses the Public IP address. The public address is needed as it provides valuable information such as "who are using your website".
- An EC2 instance gets the Ipv4 address in the form of X-Forwarded-For request Header from the Classic load balancer.
Benefits of Load Balancer in AWS:
Highly available
Elastic Load Balancing
automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple targets – Amazon EC2
instances, containers, IP addresses, and Lambda functions – in multiple
Availability Zones and ensures only healthy targets receive traffic. Elastic Load
Balancing can also load balance across a Region, routing traffic to healthy
targets in different Availability Zones. The Amazon Elastic Load Balancing
Service Level Agreement commitment is 99.99% availability for a load balancer.
Secure
Elastic Load Balancing
works with Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to provide robust security
features, including integrated certificate management, user-authentication, and
SSL/TLS decryption. Together, they give you the flexibility to centrally manage
TLS settings and offload CPU intensive workloads from your applications.
Elastic
Elastic Load Balancing is
capable of handling rapid changes in network traffic patterns. Additionally,
deep integration with Auto Scaling ensures sufficient application capacity to
meet varying levels of application load without requiring manual intervention.
Flexible
Elastic Load Balancing
also allows you to use IP addresses to route requests to application targets.
This offers you flexibility in how you virtualize your application targets, allowing
you to host more applications on the same instance. This also enables these
applications to have individual security groups and use the same network port
to further simplify inter-application communication in microservice-based
architecture.
Robust monitoring & auditing
Elastic Load Balancing
allows you to monitor your applications and their performance in real time with
Amazon CloudWatch metrics, logging, and request tracing. This improves
visibility into the behavior of your applications, uncovering issues and
identifying performance bottlenecks in your application stack at the
granularity of an individual request.
Hybrid load balancing
Elastic Load Balancing
offers ability to load balance across AWS and on-premises resources using the
same load balancer. This makes it easy for you to migrate, burst, or failover
on-premises applications to the cloud.
No comments:
Post a Comment