Creating an S3 Bucket
- Sign in to the AWS Management console. After sign in, the screen appears is shown below:
- Move to the S3 services. After clicking on S3, the screen appears is shown below:
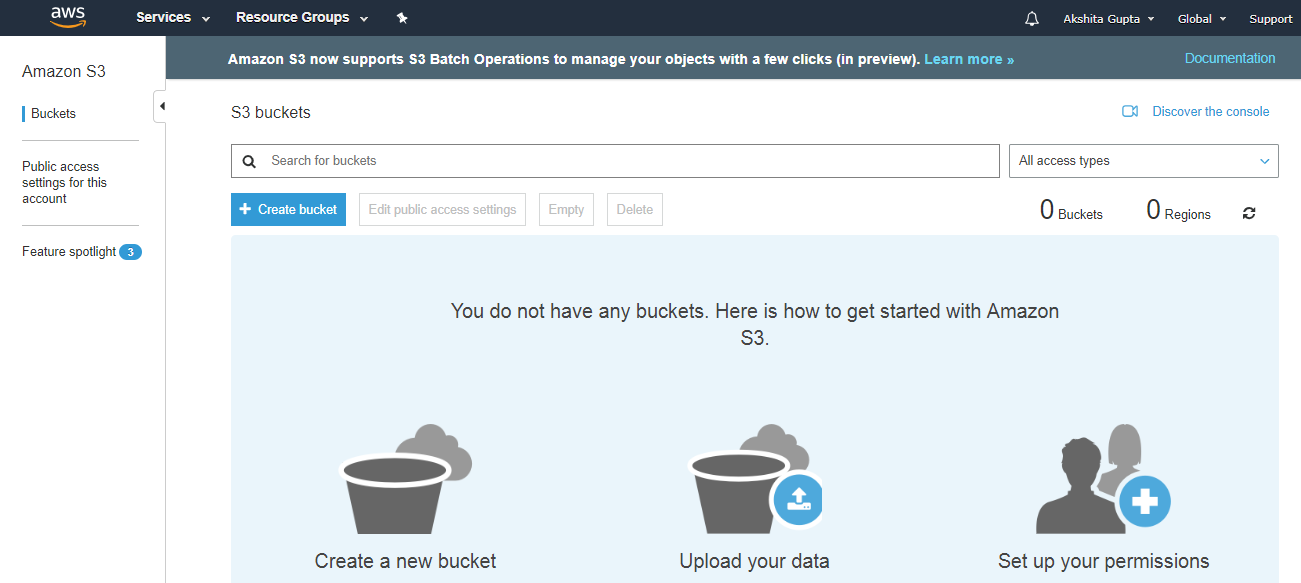
- To create an S3 bucket, click on the "Create bucket". On clicking the "Create bucket" button, the screen appears is shown below:
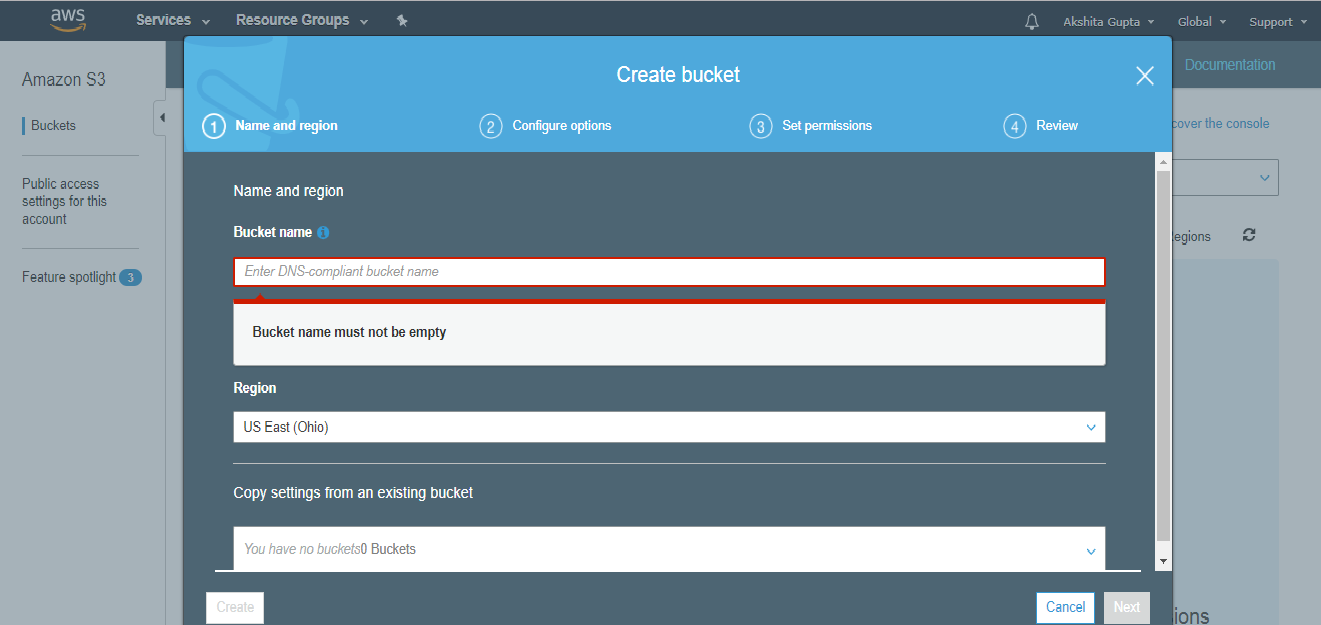
- Enter the bucket name which should look like DNS address, and it should be resolvable. A bucket is like a folder that stores the objects. A bucket name should be unique. A bucket name should start with the lowercase letter, must not contain any invalid characters. It should be 3 to 63 characters long.
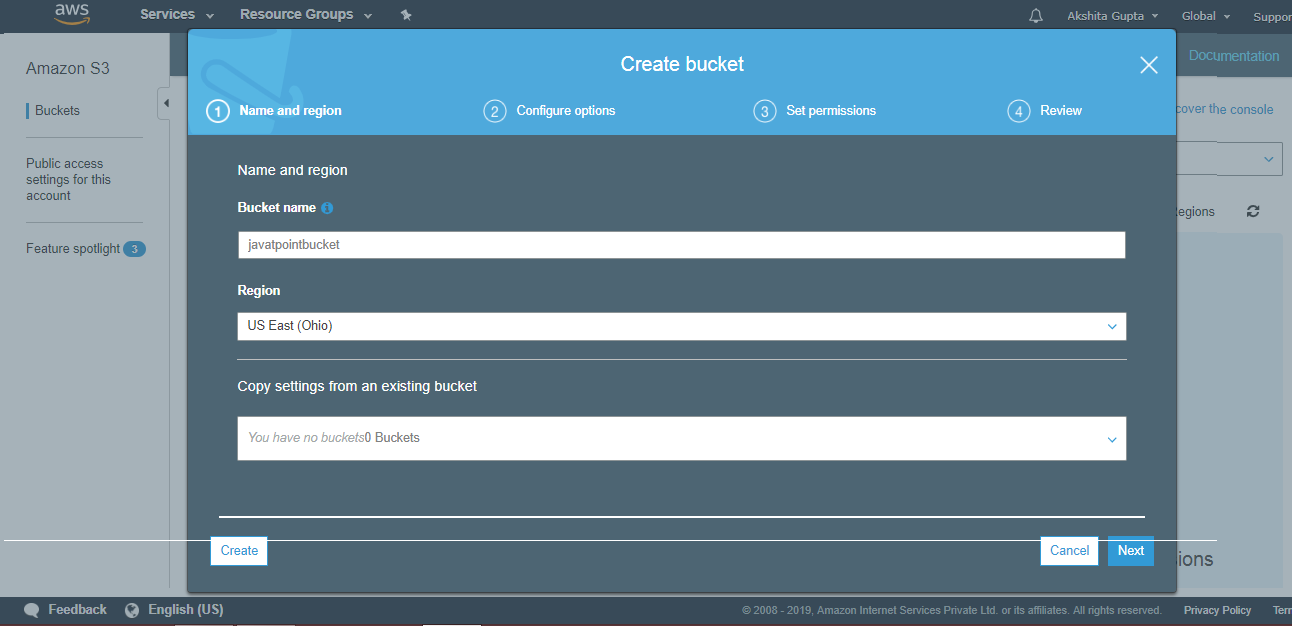
- Click on the "Create" button. Now, the bucket is created.
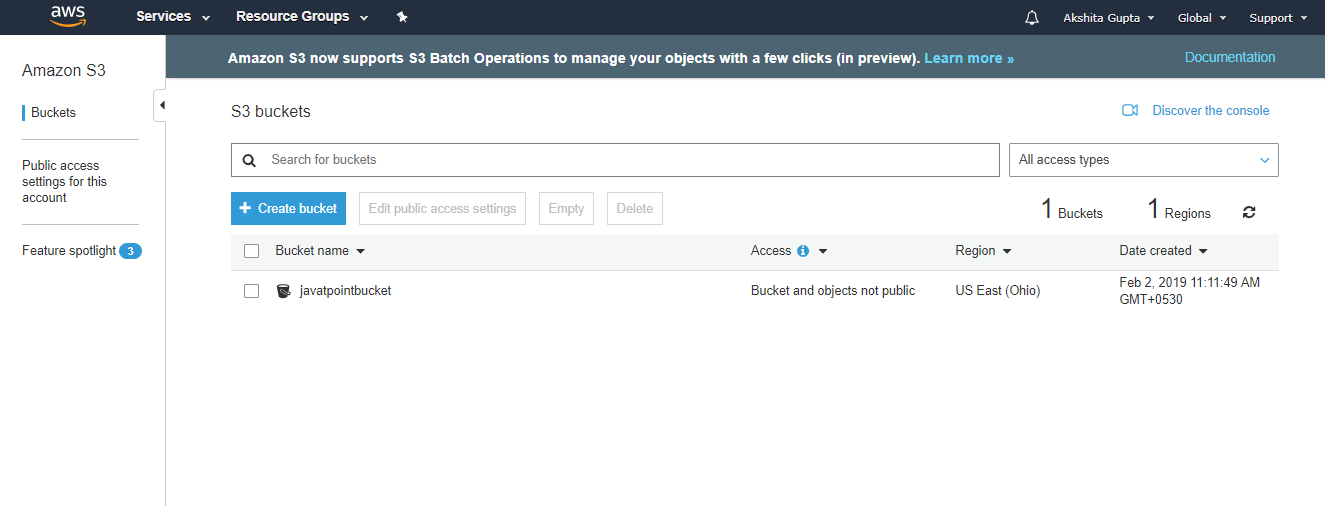
We have seen from the above screen that bucket and its objects are not public as by default, all the objects are private.
- Now, click on the "javatpointbucket" to upload a file in this bucket. On clicking, the screen appears is shown below:
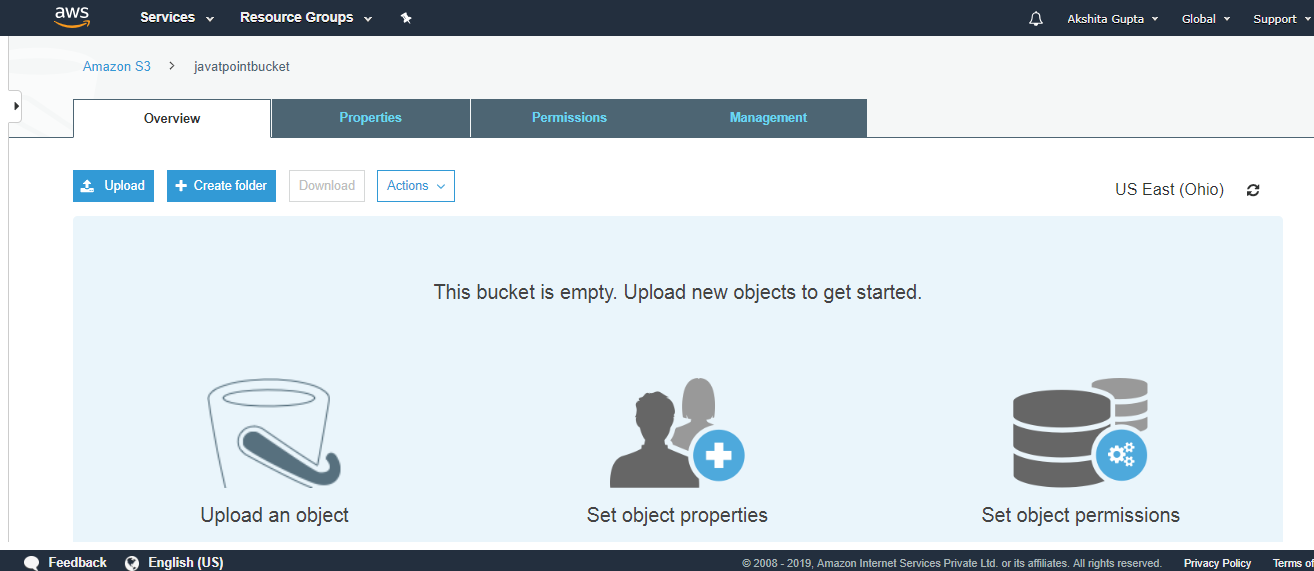
- Click on the "Upload" button to add the files to your bucket.
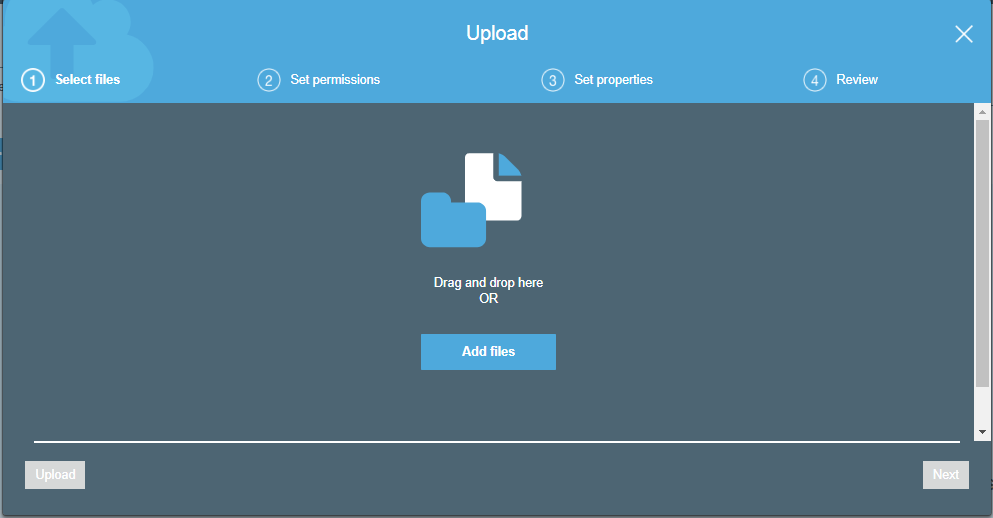
- Click on the "Add files" button.
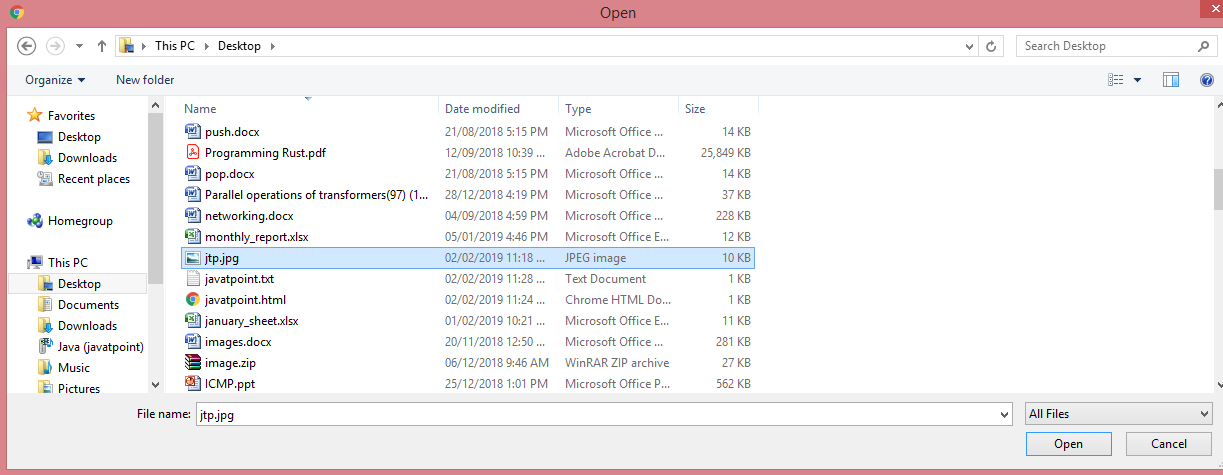
- Add the jtp.jpg file.
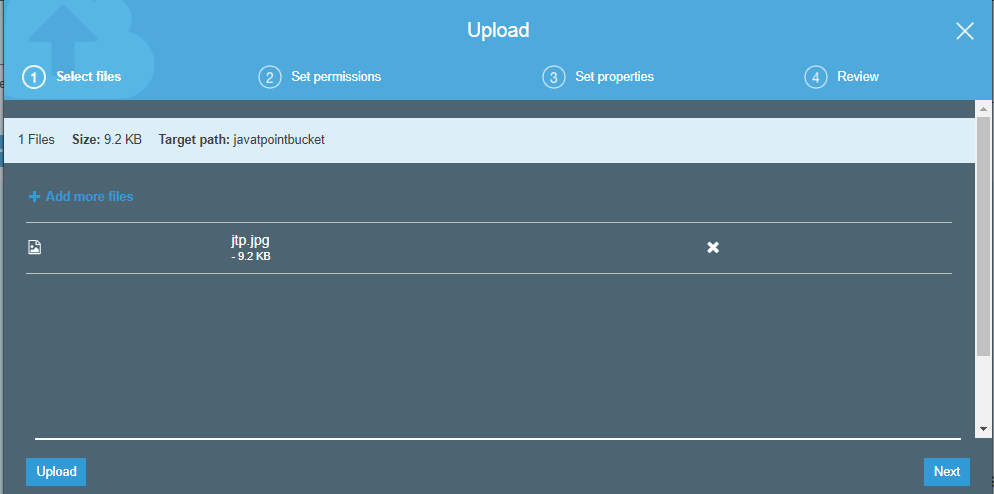
- Click on the "upload" button.
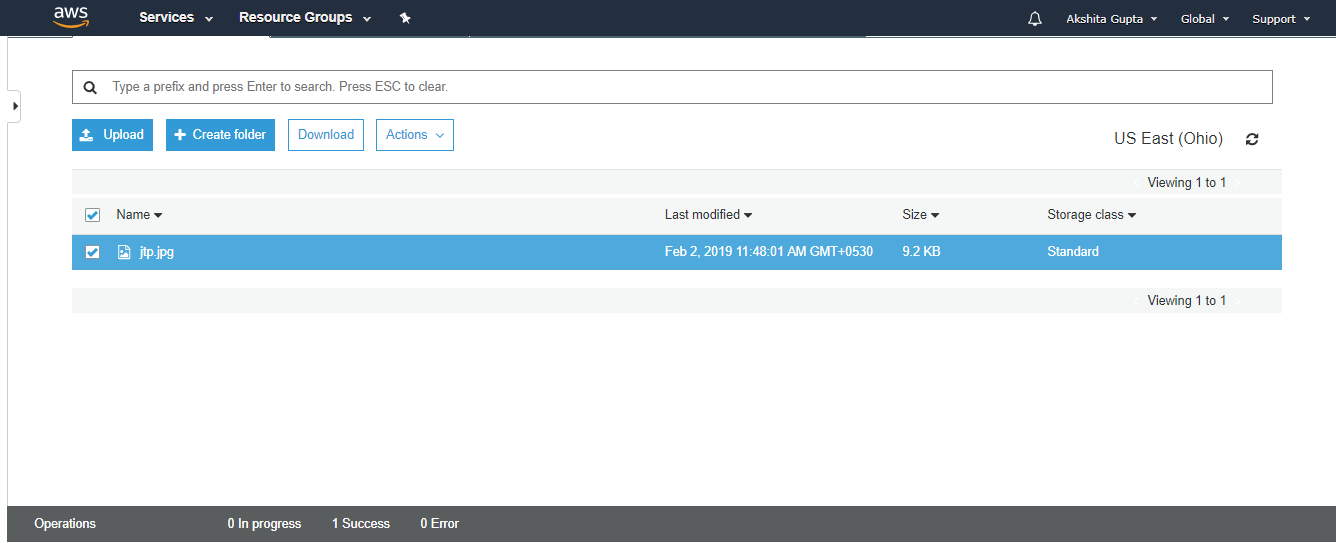
From the above screen, we observe that the "jtp.jpg" has been successfully uploaded to the bucket "javatpoint".
- Move to the properties of the object "jtp.jpg" and click on the object URL to run the file appearing on the right side of the screen
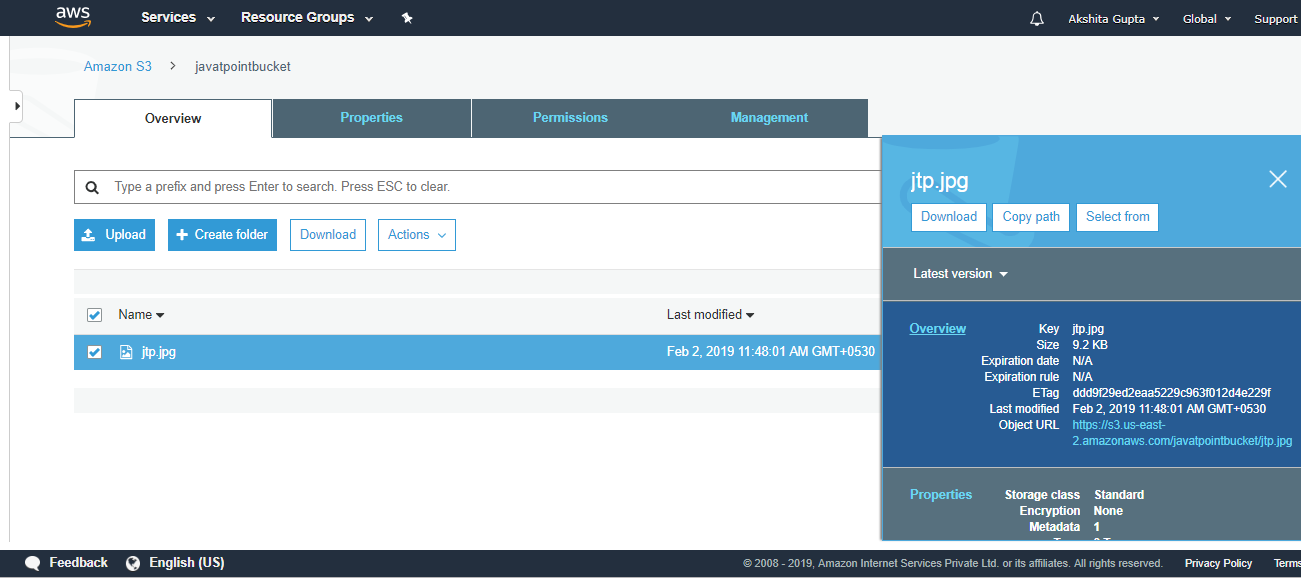
- On clicking the object URL, the screen appears is shown below:
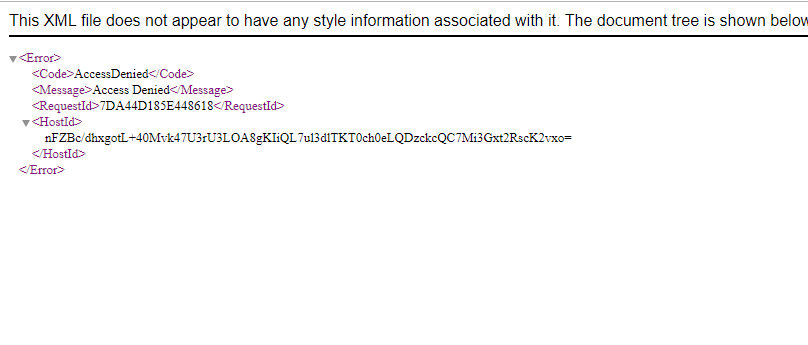
From the above screen, we observe that we are not allowed to access the objects of the bucket.
- To overcome from the above problems, we need to set the permissions of a bucket, i.e., "javatpointbucket" and unchecked all of them.
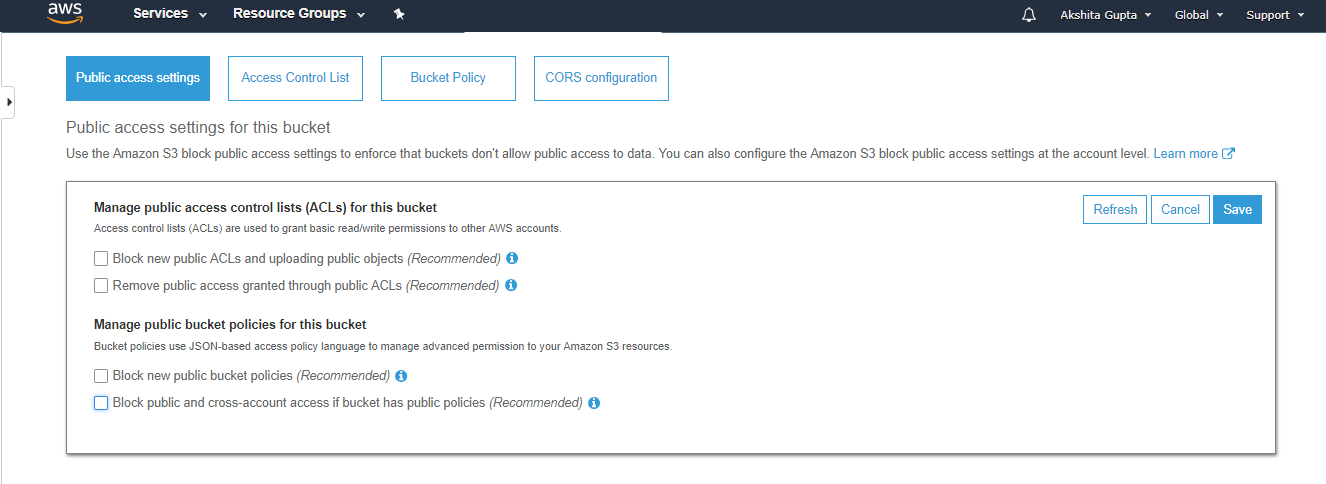
- Save these permissions.
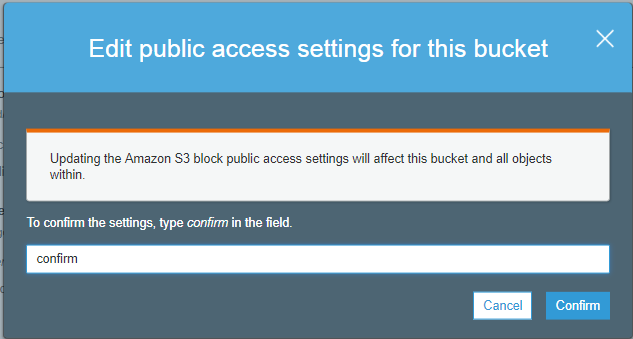
- Enter "confirm" in a textbox, then click on the "confirm" button.
- Click on the "Actions" dropdown and then click on the "Make public".
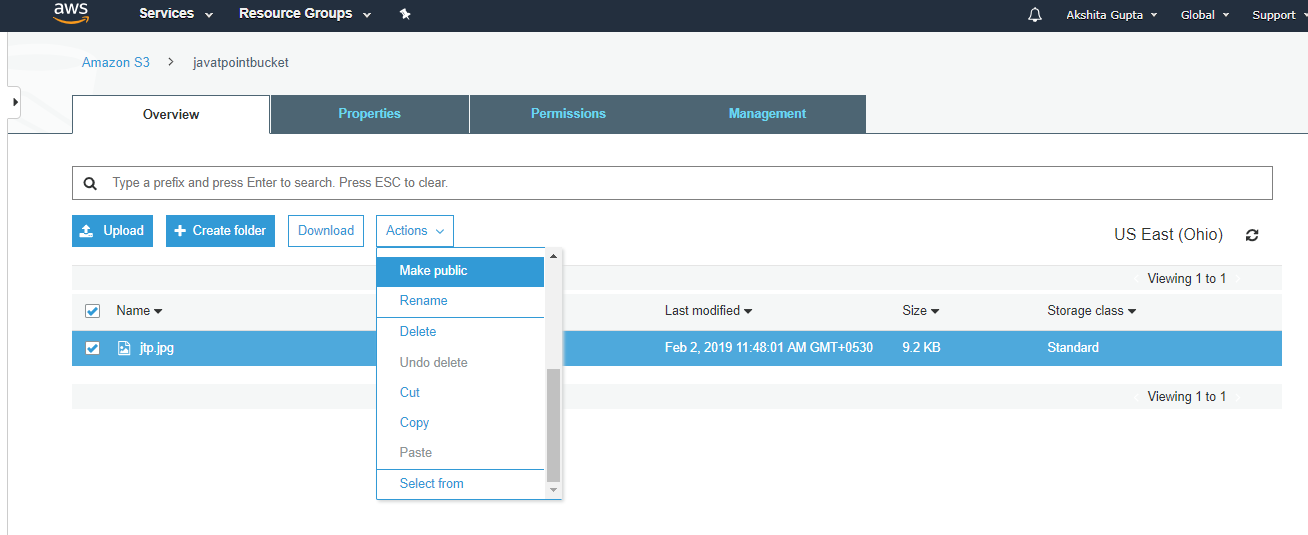
- Now, click on the Object URL of an object to run the file.
Important points to remember
- Buckets are a universal namespace, i.e., the bucket names must be unique.
- If uploading of an object to S3 bucket is successful, we receive a HTTP 200 code.
- S3, S3-IA, S3 Reduced Redundancy Storage are the storage classes.
- Encryption is of two types, i.e., Client Side Encryption and Server Side Encryption
- Access to the buckets can be controlled by using either ACL (Access Control List) or bucket policies.
- By default buckets are private and all the objects stored in a bucket are also private.
No comments:
Post a Comment