Microsoft Azure user interface
Given the dynamic nature of Microsoft cloud tools, you might experience Azure UI changes that occur after the development of this training content. As a result, the lab instructions and lab steps might not align correctly.
Microsoft updates this training course when the community alerts us to needed changes. However, cloud updates occur frequently, so you might encounter UI changes before this training content updates. If this occurs, adapt to the changes, and then work through them in the labs as needed.
Instructions
Before you start
Sign in to the lab environment
Sign in to your Windows 10 virtual machine (VM) using the following credentials:
Username: Admin
Password: Pa55w.rd
Note: Your instructor will provide instructions for connecting to the virtual lab environment.
Review the installed applications
Find the taskbar on your Windows 10 desktop. The taskbar contains the icons for the applications that you’ll use in this lab, including:
Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Visual Studio Code
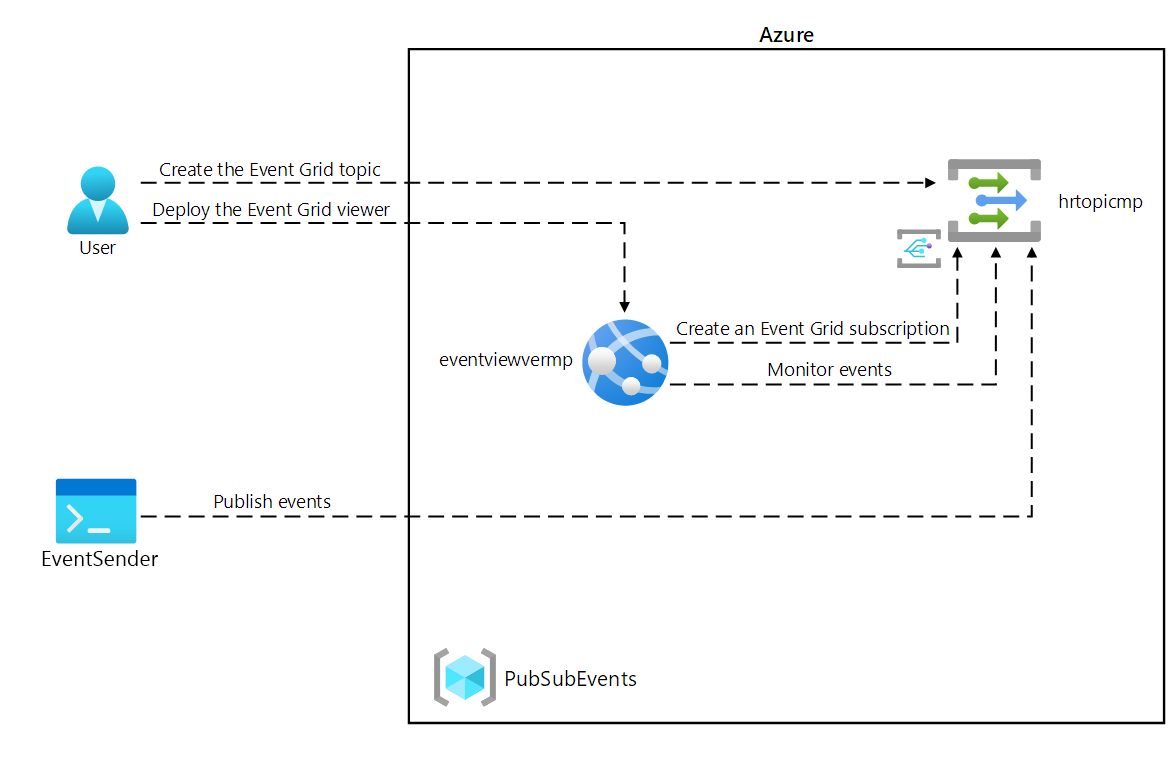
Architecture diagram
Exercise 1: Create Azure resources
Task 1: Open the Azure portal
On the taskbar, select the Microsoft Edge icon.
In the open browser window, browse to the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.com), and then sign in with the account you’ll be using for this lab.
Note: If this is your first time signing in to the Azure portal, you’ll be offered a tour of the portal. Select Get Started to skip the tour and begin using the portal.
Task 2: Open Azure Cloud Shell
In the Azure portal, select the Cloud Shell icon
 to open a new Bash session. If Cloud Shell defaults to a PowerShell session, select PowerShell and, in the drop-down menu, select Bash.
to open a new Bash session. If Cloud Shell defaults to a PowerShell session, select PowerShell and, in the drop-down menu, select Bash.Note: If this is the first time you are starting Cloud Shell, when prompted to select either Bash or PowerShell, select Bash. When you are presented with the You have no storage mounted message, select the subscription you are using in this lab, and then select Create storage.
In Azure portal, at the Cloud Shell command prompt, run the following command to get the version of the Azure Command-Line Interface (Azure CLI) tool:
Codeaz --version
Task 3: Review the Microsoft.EventGrid provider registration
In the Cloud Shell pane, run the following command to check if the resource provider “Microsoft.EventGrid” has been registered :
Codeaz provider show --namespace Microsoft.EventGrid --query "registrationState"Notice that the Microsoft.EventGrid provider has been registered.
If you got "Not Registered" status, then following this step:
Task 4: Create a custom Event Grid topic
On the Azure portal’s navigation pane, select Create a resource.
On the Create a resource blade, in the Search services and marketplace text box, enter Event Grid Topic, and then select Enter.
On the Marketplace search results blade, select the Event Grid Topic result, and then select Create.
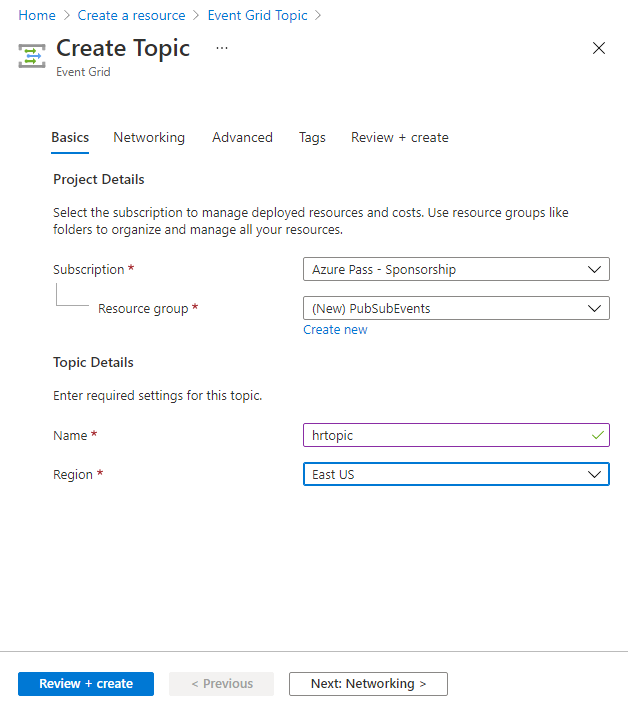
On the Create Topic blade, on the Basics tab, perform the following actions, and then select the Advanced tab:
Setting Action Subscription drop-down list Retain the default value Resource group drop-down list Select Create new, enter PubSubEvents, and then select OK Name text box Enter hrtopic[yourname] Region drop-down list Select East US The following screenshot displays the configured settings on the Basics tab.
On the Advanced tab, from the Event Schema drop-down list, select Event Grid Schema, and then select Review + create.
On the Review + create tab, review the options that you selected during the previous steps.
Select Create to create the event grid topic by using your specified configuration.
Note: Wait for Azure to finish creating the topic before you continue with the lab. You’ll receive a notification when the topic is created.
Task 5: Deploy the Azure Event Grid viewer to a web app
On the Azure portal’s navigation pane, select Create a resource.
On the Create a resource blade, in the Search services and marketplace text box, enter Web App, and then select Enter.
On the Marketplace search results blade, select the Web App result, and then select Create.
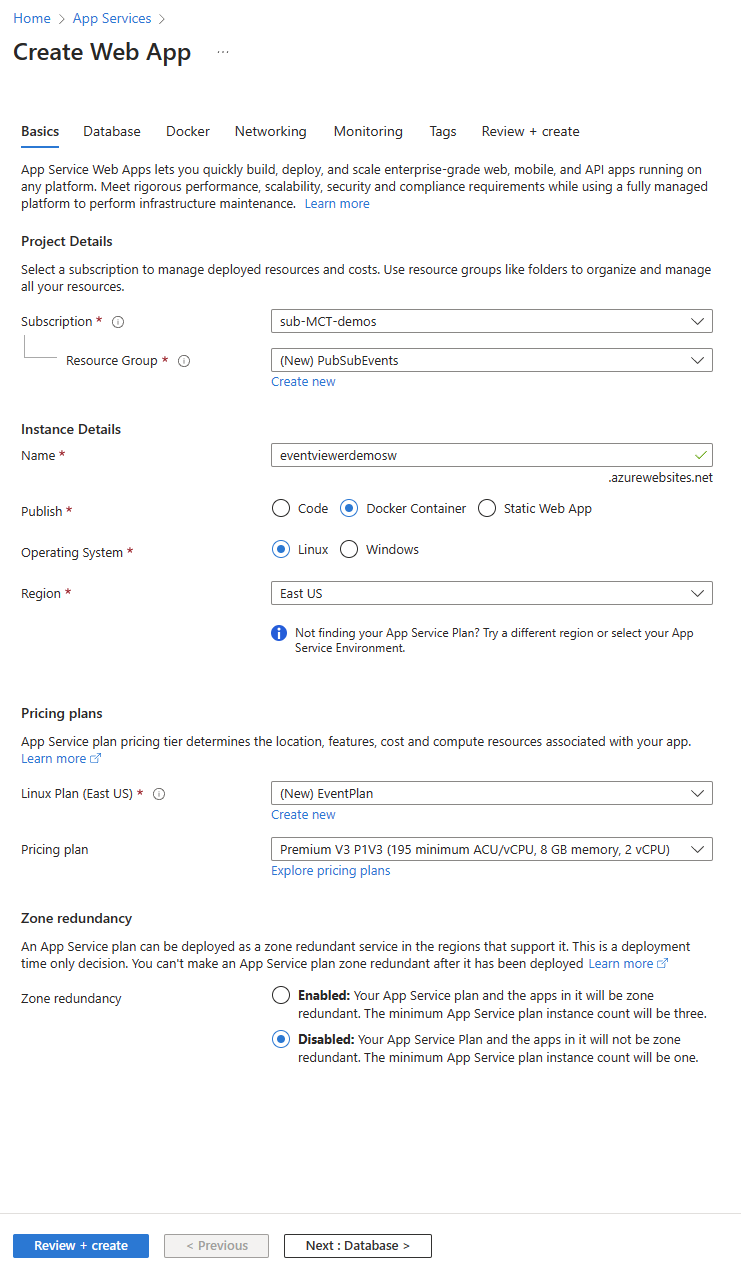
On the Create Web App blade, on the Basics tab, perform the following actions, and then select Next: Docker:
Setting Action Subscription drop-down list Retain the default value Resource group drop-down list Select PubSubEvents in the list Name text box Enter eventviewer[yourname] Publish section Select Docker Container Operating System section select Linux Region drop-down list Select **East US Linux Plan (East US) section Select Create new, in the Name text box, enter EventPlan, and then select OK SKU and size section Retain the default value The following screenshot displays the configured settings on the Create Web App blade.
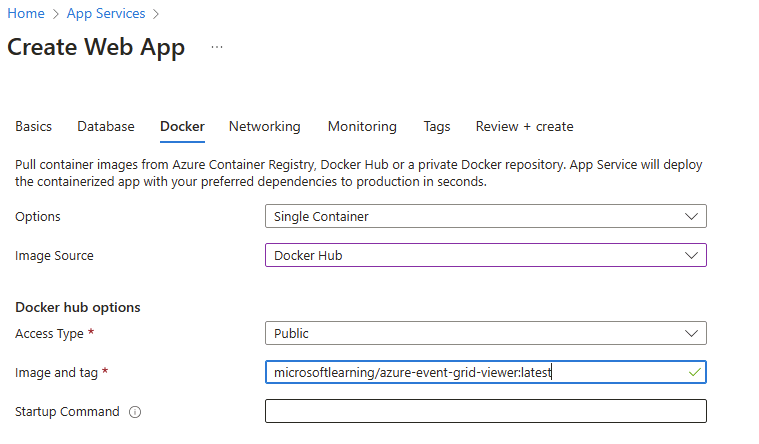
On the Docker tab, perform the following actions, and select Review + create:
Setting Action Options drop-down list Select Single Container Image Source drop-down list Select Docker Hub Access Type drop-down list Select Public Image and tag text box Enter microsoftlearning/azure-event-grid-viewer:latest The following screenshot displays the configured settings on the Docker tab.
On the Review + create tab, review the options that you selected during the previous steps.
Select Create to create the web app using your specified configuration.
Note: Wait for Azure to finish creating the web app before you continue with the lab. You’ll receive a notification when the app is created.
Review
In this exercise, you created the Event Grid topic and a web app that you will use throughout the remainder of the lab.
Exercise 2: Create an Event Grid subscription
Task 1: Access the Event Grid Viewer web application
On the Azure portal’s navigation pane, select Resource groups.
On the Resource groups blade, select the PubSubEvents resource group.
On the PubSubEvents blade, select the eventviewer[yourname] web app.
On the App Service blade, in the Settings category, select the Properties link.
In the Properties section, record the value of the URL link. You’ll use this value later in the lab.
Select Overview, and then select Browse.
Observe the currently running Azure Event Grid Viewer web application. Leave this web application running for the remainder of the lab.
Note: This web application will update in real time as events are sent to its endpoint. You’ll use this application to monitor events throughout the lab.
Return to your currently open browser window that displays the Azure portal.
Task 2: Create a new subscription
On the Azure portal’s navigation pane, select Resource groups.
On the Resource groups blade, select the PubSubEvents resource group that you created previously in this lab.
On the PubSubEvents blade, select the hrtopic[yourname] Event Grid topic that you created previously in this lab.
On the Event Grid Topic blade, select + Event Subscription.
On the Create Event Subscription blade, perform the following actions, and then select Create:
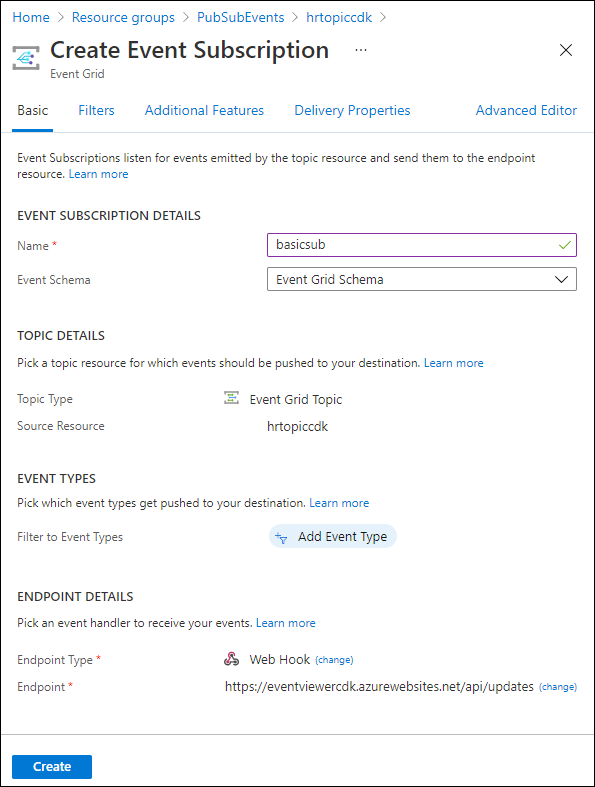
Setting Action Name text box Enter basicsub Event Schema drop-down list Select Event Grid Schema Endpoint Type drop-down list Select Web Hook Endpoint Select Select an endpoint. In the Subscriber Endpoint text box, enter the Web App URL value that you recorded previously, ensure that it uses an https:// prefix, add the suffix /api/updates, and then select Confirm Selection. For example, if your Web App URL value is http://eventviewerstudent.azurewebsites.net/, then your Subscriber Endpoint would behttps://eventviewerstudent.azurewebsites.net/api/updatesThe following screenshot displays the configured settings on the Create Event Subscription blade.
Note: Wait for Azure to finish creating the subscription before you continue with the lab. You’ll receive a notification when the subscription is created.
Task 3: Observe the subscription validation event
Return to the browser window displaying the Azure Event Grid Viewer web application.
Review the Microsoft.EventGrid.SubscriptionValidationEvent event that was created as part of the subscription creation process.
Select the event and review its JSON content.
Return to your currently open browser window with the Azure portal.
Task 4: Record subscription credentials
On the Azure portal’s navigation pane, select Resource groups.
On the Resource groups blade, select the PubSubEvents resource group that you created previously in this lab.
On the PubSubEvents blade, select the hrtopic[yourname] Event Grid topic that you created previously in this lab.
On the Event Grid Topic blade, record the value of the Topic Endpoint field. You’ll use this value later in the lab.
In the Settings category, select the Access keys link.
In the Access keys section, record the value of the Key 1 text box. You’ll use this value later in the lab.
Review
In this exercise, you created a new subscription, validated its registration, and then recorded the credentials required to publish a new event to the topic.
Exercise 3: Publish Event Grid events from .NET
Task 1: Create a .NET project
On the Start screen, select the Visual Studio Code tile.
On the File menu, select Open Folder.
In the File Explorer window that opens, browse to Allfiles (F):\Allfiles\Labs\09\Starter\EventPublisher, and then select Select Folder.
In the Visual Studio Code window, from its top menu bar, go to Terminal menu and select New Terminal.
Run the following command to create a new .NET project named EventPublisher in the current folder:
Codedotnet new console --framework net6.0 --name EventPublisher --output .Note: The dotnet new command will create a new console project in a folder with the same name as the project.
Run the following command to import version 4.11.0 of Azure.Messaging.EventGrid from NuGet:
Codedotnet add package Azure.Messaging.EventGrid --version 4.11.0Note: The dotnet add package command will add the Microsoft.Azure.EventGrid package from NuGet. For more information, go to Azure.Messaging.EventGrid.
Run the following command to build the .NET web application:
Codedotnet buildSelect Kill Terminal or the Recycle Bin icon to close the currently open terminal and any associated processes.
Task 2: Modify the Program class to connect to Event Grid
On the Explorer pane of the Visual Studio Code window, open the Program.cs file.
On the code editor tab for the Program.cs file, delete all the code in the existing file.
Add the following line of code to import the Azure, and Azure.Messaging.EventGrid namespaces from the Azure.Messaging.EventGrid package imported from NuGet:
C#using Azure; using Azure.Messaging.EventGrid;Add the following lines of code to add using directives for the built-in namespaces that will be used in this file:
C#using System; using System.Threading.Tasks;Enter the following code to create a new Program class:
C#public class Program { }In the Program class, enter the following line of code to create a new string constant named topicEndpoint:
C#private const string topicEndpoint = "";Update the topicEndpoint string constant by setting its value to the Topic Endpoint of the Event Grid topic that you recorded previously in this lab.
In the Program class, enter the following line of code to create a new string constant named topicKey:
C#private const string topicKey = "";Update the topicKey string constant by setting its value to the Key of the Event Grid topic that you recorded previously in this lab.
In the Program class, enter the following code to create a new asynchronous Main method:
C#public static async Task Main(string[] args) { }Observe the Program.cs file, which should now include the following lines of code:
C#using Azure; using Azure.Messaging.EventGrid; using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; public class Program { private const string topicEndpoint = "<topic-endpoint>"; private const string topicKey = "<topic-key>"; public static async Task Main(string[] args) { } }
Task 3: Publish new events
In the Main method, perform the following actions to publish a list of events to your topic endpoint:
a. Add the following line of code to create a new variable named endpoint of type Uri, using the topicEndpoint string constant as a constructor parameter:
C#Uri endpoint = new Uri(topicEndpoint);b. Add the following line of code to create a new variable named credential of type AzureKeyCredential, using the topicKey string constant as a constructor parameter:
C#AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(topicKey);c. Add the following line of code to create a new variable named client of type EventGridPublisherClient, using the endpoint and credential variables as constructor parameters:
C#EventGridPublisherClient client = new EventGridPublisherClient(endpoint, credential);d. Add the following block of code to create a new variable named firstEvent of type EventGridEvent and populate that variable with sample data:
C#EventGridEvent firstEvent = new EventGridEvent( subject: $"New Employee: Alba Sutton", eventType: "Employees.Registration.New", dataVersion: "1.0", data: new { FullName = "Alba Sutton", Address = "4567 Pine Avenue, Edison, WA 97202" } );e. Add the following block of code to create a new variable named secondEvent of type EventGridEvent and populate that variable with sample data:
C#EventGridEvent secondEvent = new EventGridEvent( subject: $"New Employee: Alexandre Doyon", eventType: "Employees.Registration.New", dataVersion: "1.0", data: new { FullName = "Alexandre Doyon", Address = "456 College Street, Bow, WA 98107" } );f. Add the following line of code to asynchronously invoke the EventGridPublisherClient.SendEventAsync method using the firstEvent variable as a parameter:
C#await client.SendEventAsync(firstEvent);g. Add the following line of code to render the “First event published” message to the console:
C#Console.WriteLine("First event published");h. Add the following line of code to asynchronously invoke the EventGridPublisherClient.SendEventAsync method using the secondEvent variable as a parameter:
C#await client.SendEventAsync(secondEvent);i. Add the following line of code to render the “Second event published” message to the console:
C#Console.WriteLine("Second event published");Review the Main method, which should now include:
C#public static async Task Main(string[] args) { Uri endpoint = new Uri(topicEndpoint); AzureKeyCredential credential = new AzureKeyCredential(topicKey); EventGridPublisherClient client = new EventGridPublisherClient(endpoint, credential); EventGridEvent firstEvent = new EventGridEvent( subject: $"New Employee: Alba Sutton", eventType: "Employees.Registration.New", dataVersion: "1.0", data: new { FullName = "Alba Sutton", Address = "4567 Pine Avenue, Edison, WA 97202" } ); EventGridEvent secondEvent = new EventGridEvent( subject: $"New Employee: Alexandre Doyon", eventType: "Employees.Registration.New", dataVersion: "1.0", data: new { FullName = "Alexandre Doyon", Address = "456 College Street, Bow, WA 98107" } ); await client.SendEventAsync(firstEvent); Console.WriteLine("First event published"); await client.SendEventAsync(secondEvent); Console.WriteLine("Second event published"); }Save the Program.cs file.
In the Visual Studio Code window, activate the shortcut menu for the Explorer pane, and then select Open in Integrated Terminal.
Run the following command to run the .NET web application:
Codedotnet runNote: If there are any build errors, review the Program.cs file in the Allfiles (F):\Allfiles\Labs\09\Solution\EventPublisher folder.
Observe the success message output from the currently running console application.
Select Kill Terminal or the Recycle Bin icon to close the currently open terminal and any associated processes.
Task 4: Observe published events
Return to the browser window with the Azure Event Grid Viewer web application.
Review the Employees.Registration.New events that were created by your console application.
Select any of the events and review its JSON content.
Return to the Azure portal.
Review
In this exercise, you published new events to your Event Grid topic by using a .NET console application.
Exercise 4: Clean up your subscription
Task 1: Open Azure Cloud Shell
In the Azure portal, select the Cloud Shell icon
 to open a new Bash session. If Cloud Shell defaults to a PowerShell session, select PowerShell and, in the drop-down menu, select Bash.
to open a new Bash session. If Cloud Shell defaults to a PowerShell session, select PowerShell and, in the drop-down menu, select Bash.Note: If this is the first time you are starting Cloud Shell, when prompted to select either Bash or PowerShell, select PowerShell. When you are presented with the You have no storage mounted message, select the subscription you are using in this lab, and select Create storage.
Task 2: Delete a resource group
On the Cloud Shell pane, run the following command to delete the PubSubEvents resource group:
Codeaz group delete --name PubSubEvents --no-wait --yesNote: The command runs asynchronously (as determined by the –no-wait parameter), so while you’ll be able to run another Azure CLI command immediately afterwards within the same Bash session, it’ll take a few minutes before the resource groups are actually removed.
Close the Cloud Shell pane in the portal.
Task 3: Close the active applications
Close the currently running Microsoft Edge application.
Close the currently running Visual Studio Code application.